Acid-Fast Stain Protocols - Ziehl-Neelsen, Kinyoun, Truant Methods
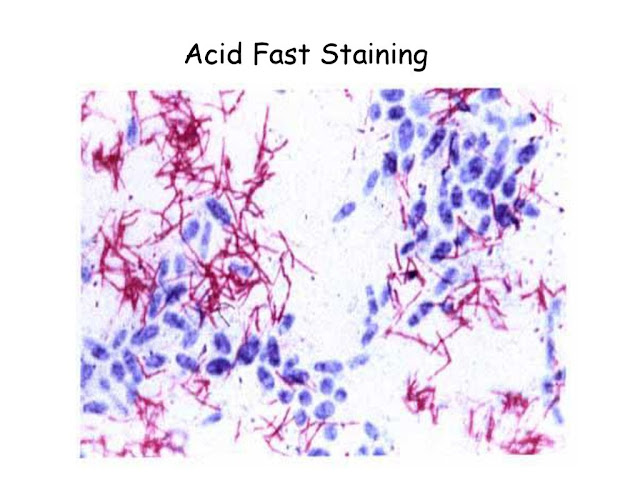
There are three common acid-fast staining methods, Ziehl-Neelsen (hot), Kinyoun (cold), and Auramine-Rhodamine Fluorochrome (Truant method). The Ziehl-Neelsen method has endured as a reliable and effective way to demonstrate the acid-fast bacteria. In 1882 Robert Koch reported the discovery of the tubercle bacillus (4) and described the appearance of the bacilli resulting from a complex staining procedure. During the same time period several other researchers (Ehrlich, Ziehl, Rindfleisch, and Neelsen), intending to improve on Koch’s method, introduced modifications to the reagents and the procedure. Franz Ziehl was the first to use carbolic acid (phenol) as the mordant. Friedrich Neelsen kept Ziehl’s mordant, but changed the primary stain to the basic fuchsin (first used by Ehrlich in 1882). This method became known as the Ziehl-Neelsen method in the early to mid 1890s. In this method heat is used to help drive the primary stain into the waxy cell walls of these difficult-to-s
